Classified Balance Sheet Format Examples Explanation

As a financial statement, the classified balance sheet presents a company’s assets and liabilities in organized categories, typically dividing them into current and non-current (or long-term) sections. This categorization aids stakeholders in understanding a company’s short-term liquidity and long-term solvency, providing a detailed snapshot of its financial health at a specific time. The classified balance sheet is a roadmap for financial analysis and business decision-making. The categorization of assets and liabilities into current and non-current provides stakeholders with valuable insights into the company’s financial health, both short-term and long-term.
Shareholder’s Equity or Owner’s Equity:
By understanding the breakdown of current and non-current assets and liabilities, they can better plan for the company’s financial needs and growth opportunities. It also checks if the company has enough to pay its debts soon through the current ratio and keeps track of payables classified balance sheet template and services. Just like organizing our toy box makes playtime better, a classified balance sheet helps everyone understand the company’s financial health. Classified balance sheets provide a granular view of a company’s financial standing, allowing for more in-depth analysis.
Investors – The Global Perspective
It should be customized to include the specific asset and liability categories that apply to your company. The report form balance sheet is presented in a vertical variation and is essentially one column that spans the entire width of the page. The benefits of using a report form balance sheet include its ability to showcase the fiscal year in one report. Typically, when assets are greater than liabilities, this represents a strong financial position. But when liabilities are greater than assets, this can represent a weak financial position and a company with lower value.
Organizing Assets by Current and Non-Current Categories
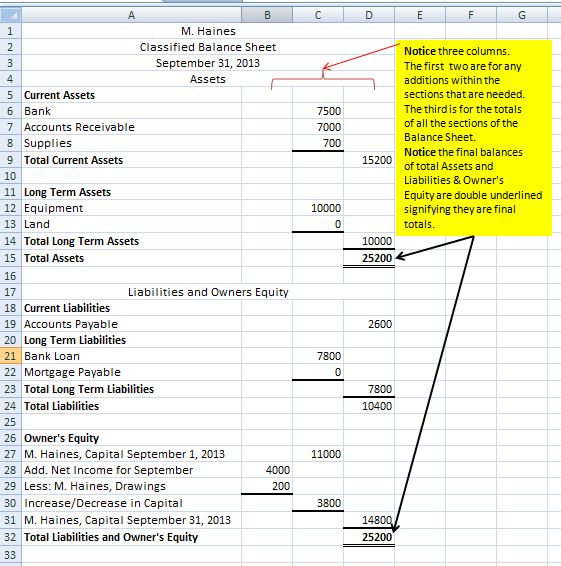
This data is instrumental in assessing risk, making investment decisions, and planning for future growth or consolidation. Classified Balance Sheet is often use by companies to improve users’ understanding of a company’s financial position. Financial Statements of the company show its financial health, position and its operational activities.
- These are the assets that should be sold or consumed to use cash well within the current operating cycle.
- A classified balance sheet is identical to a traditional balance sheet.
- The equity section represents the owners’ interest in the business and typically includes common stock, retained earnings, and treasury stock.
- When you subtract your liabilities from your assets ($14,000 – 7,000), the remainder ($7,000) is your owners’ equity.
Liabilities
A classified balance sheet format provides a crisp and crystal clear view to the reader. Although balance sheets are prepared they are read by normal investors who might not have an accounting background. The different subcategories help an investor understand the importance of a particular entry in the balance sheet and why it has been placed there. It also helps investors in their financial analysis and makes suitable decisions for their investments. A classified balance sheet is a financial statement that shows a company’s assets, liabilities, and ownership details, but with a twist. It puts these items into different categories so they are easier to understand.
With the globalization of business, understanding the nuances in balance sheets from a worldwide perspective is essential. A classified balance sheet goes beyond the standard balance sheet by sorting assets and liabilities into more specific classes. The main advantage of this detailed classification is that it offers stakeholders a more nuanced view of a company’s financial condition. The classified balance sheet is the most detailed among all types of balance sheets. When a detailed balance sheet with up-to-date information about the business’s financial position is published, it increases the trust of investors and creditors. The creditors and investors have all the required information to decide about investment or issuing loans.
This detailed view can then be used to analyze the business’s liquidity, solvency, and overall financial health. This kind of analysis wouldn’t be easy with a traditional balance sheet that isn’t grouped into current and long-term classifications. Small organizations use an unclassified balance sheet, but if you’re searching for a report that gives similar information in a more definite form, you’ll need to set up a classified balance sheet. A classified balance sheet has liability, asset, and equity sections in subcategories for ease in usability.
The total amounts will automatically populate, based on the embedded formulas. Get a close-up view of how accounting on Salesforce can eliminate the need for costly integrations—and silos of mismatched information—by sharing the same database as your CRM. Fair disclosure is also one of the benefits offered by a classified balance sheet. In any balance sheet, it is possible to misrepresent information or misstate the facts.
For example, a tech company may have a significant portion of intangible assets like patents and software. In contrast, a manufacturing company might have a more extensive inventory and more substantial tangible assets like machinery. A higher amount of current liabilities than current assets can be a red flag, suggesting potential liquidity issues. They include accounts payable, short-term loans, and other similar debts. These are assets that a company expects to convert into cash or use within a year. Common examples include cash, cash equivalents, accounts receivable, and inventory.
It facilities the company to easily identify and makes any potential changes or make a decision regarding investing in current or fixed assets and deciding the source and mix of financing. Moreover, it enables the users to easily calculate ratios for financial statement analysis that uses items of balance sheet for calculating ratios like acid test ratios. A Classified Balance Sheet is a financial statement where the balances of assets, liabilities, and equity are grouped into meaningful categories. This helps stakeholders quickly assess the company’s liquidity, operational efficiency, and capital structure. The classification is typically done by grouping assets and liabilities into current and long-term categories.
The equation will likewise remain the same in the classified balance sheet. This implies that when you add all groups of assets, it will be equal to the sum of all categories of equity and liabilities. Both a classified and an unclassified balance sheet should stick to this equation, regardless of how basic or complex the balance sheet is. These are the assets that should be sold or consumed to use cash well within the current operating cycle. These are basically required to support the day-by-day tasks or the core business of the firm. A significant feature is that these can be easily liquidated to generate cash, which helps a business in managing any financial liquidity crunches.
